Big data can be quite a confusing concept to grasp. What's considered big data and what's not so big data?
While big data is still data, it requires a different engineering approach and not just because of its size. Big data is tons of mixed, unstructured information that keeps piling up at high speed. That’s why traditional data transportation methods can’t efficiently manage the big data flow. Big data fosters the development of new tools for transporting, storing, and analyzing vast amounts of unstructured data.
Prominent enterprises in numerous sectors including sales, marketing, research, and healthcare are actively collecting big data. At the same time, they are facing a shortage of the necessary expertise. That’s why a data specialist with big data skills is one of the most sought-after IT candidates.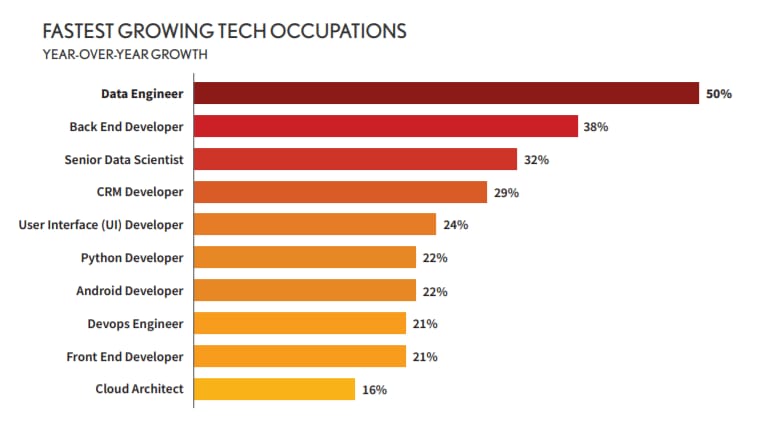
Data Engineering positions have grown by half and they typically require big data skills. In 2020 the average time to fill a Big Data Engineer position is about to increase as more companies compete for available talent to handle their big data infrastructure, Source: Dice Tech Job Report 2020
Data engineering vs big data engineering
In our article on data engineering, we give a detailed description of data processing. Here, we’ll provide a brief recap or you may watch our explainer video.

Data engineering 101
Generally, a data engineer extracts data from different sources, transforms it, and loads it on a central repository aka data warehouse, where it’s stored ready to be used by the data science team for further analysis. Abbreviated, this process is called ETL, the foundation of pipeline infrastructure - how data travels from data sources to a data warehouse.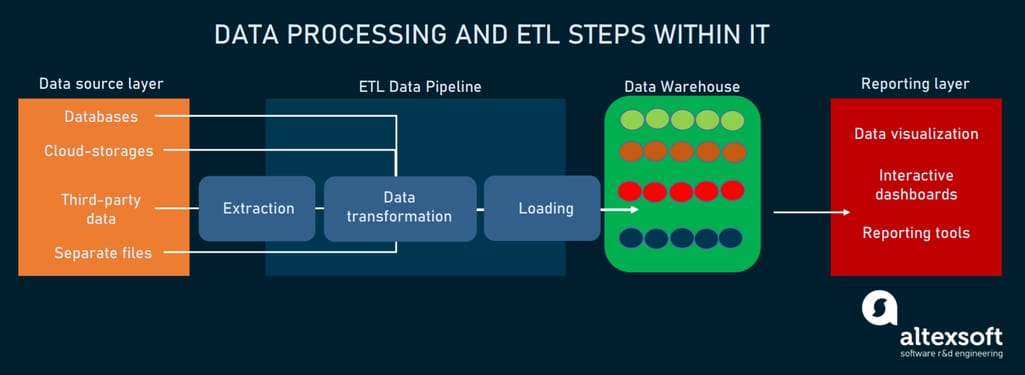
Regular data processing
However, when it comes to big data, such infrastructure isn’t capable of facilitating its volume. This drives the main difference between data engineering and big data engineering, namely:
- A data warehouse is often replaced by a data lake where big data engineers modify the sequence of ETL operations.
- Loading starts immediately after extracting data, so a data lake stores data in its native format in contrast to the warehouse where data is already processed and ready for use. That’s very convenient if data scientists haven’t yet decided on its further use. So, once they make up their minds, they can easily access and process a selected data chunk on demand. This greatly increases data processing capabilities.
- Data lakes have much larger storage capacity. So, storing a lot of raw data, they risk mutating into data swamps. To prevent that, big data engineers must carefully exercise appropriate data quality and data governance measures. For instance, giving unique identifiers and metadata tags to every data element.
- Having very few limitations, data lakes are flexible in terms of making changes to data.
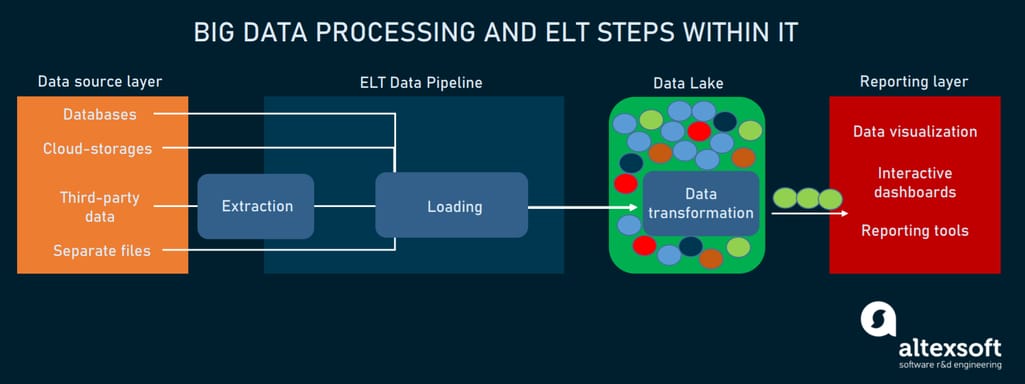
Big data processing
Now that we’ve defined the scope of big data engineering, we can go to observing the role of a big data engineer. Staying behind the scenes, the importance of a big data engineer's work is sometimes underestimated. But like the people building roads and bridges, big data engineers do first and foremost work developing and maintaining big data infrastructure.
You can see a brief list of their responsibilities, skills, and tools. Next, we’ll review them in more detail.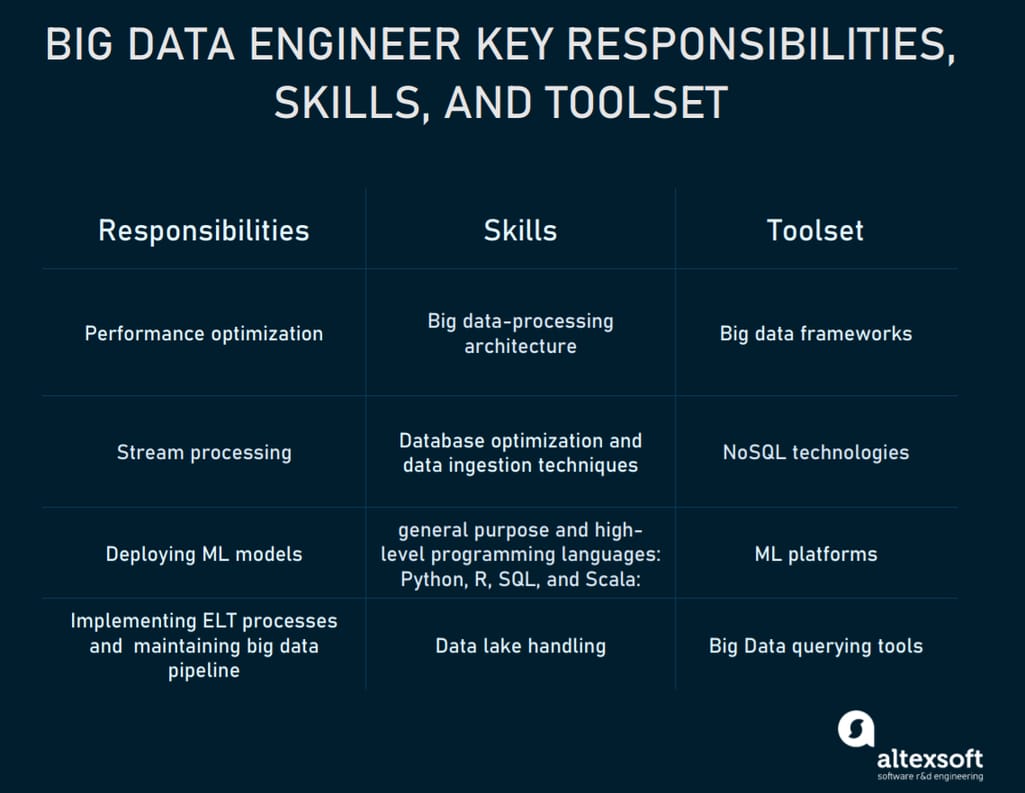
The role of a big data engineer
Big data engineer responsibilities
A big data engineer's core functions are similar to a data engineer’s:
- designing the architecture of a big data platform
- maintaining and orchestrating data pipelines
- customizing and managing integration tools, databases, warehouses, and analytical systems
- managing and structuring data
- setting up data-access tools for data scientists
However, a big data engineer's responsibilities have peculiarities in terms of dealing with big data. Let’s have a look at them.
Performance optimization
Dealing with big data platforms, performance becomes a major factor. Big data engineers need to monitor the complete process and apply necessary infrastructure changes to speed up the query execution. This includes using the following.
Database optimization techniques. One of them is data partitioning, breaking and storing data in independent, self-contained subsets. Each data chunk gets a partition key for a fast lookup. Another technique, database indexing, is a way of structuring data to speed up data retrieval operations in large tables. Big data engineers do denormalization to reduce the number of joins on tables by adding redundant data to one or more tables.
Efficient data ingestion. When it comes to constantly accelerating data in various formats, its transportation gets more complex. Discovering patterns in data sets with data mining techniques and using different data ingestion APIs, big data engineers can capture and inject more data into the data lake.
Stream processing
Setting up and managing streaming flows is one of the most commonplace occupations of big data engineers today.
Businesses are widely leveraging transactional data, IoT devices, and hardware sensors. What’s so peculiar about data streams is their continuous flow with constant updates that lose their relevance shortly. So, such data requires immediate processing. A common batch processing approach won’t do here. There’s no time for uploading data streams into storage and only then process them. It takes another approach - concurrent processing of multiple streams. Big data engineers feed data streams to event stream processors that simultaneously process data, keep it updated, and constantly bring it to the user.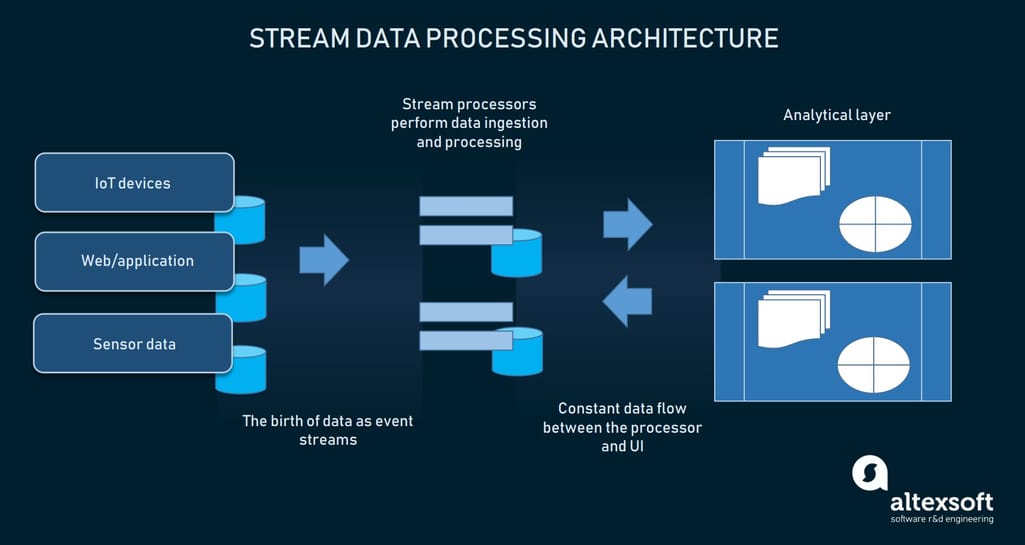
How stream processing works
Deploying ML models
Although it’s not a primary skill for a big data engineer, they are often involved in the deployment process if a data scientist isn’t skilled in producing production-ready code and building it in the pipeline. For example, we have streaming images and we need to classify them in the pipeline before storing. In this case, a big data engineer has to deploy a corresponding ML model in the data pipeline.
Big data engineer skills and toolset
Big data engineers have considerable knowledge of Java and extensive coding experience in general purpose and high-level programming languages such as Python, R, SQL, and Scala.
If you compare different big data engineer job descriptions, you’ll find that most of them are based on the knowledge of specific tools and technologies. So, a big data engineer has to learn multiple frameworks and NoSQL databases to create, design, and manage the processing systems.
Big data processing frameworks
Frameworks for computing over the data in the system can be classified by the type of data analysis they perform. So, we’ve got batch-only Hadoop, stream-only Storm and Samza, and hybrid Spark and Flink.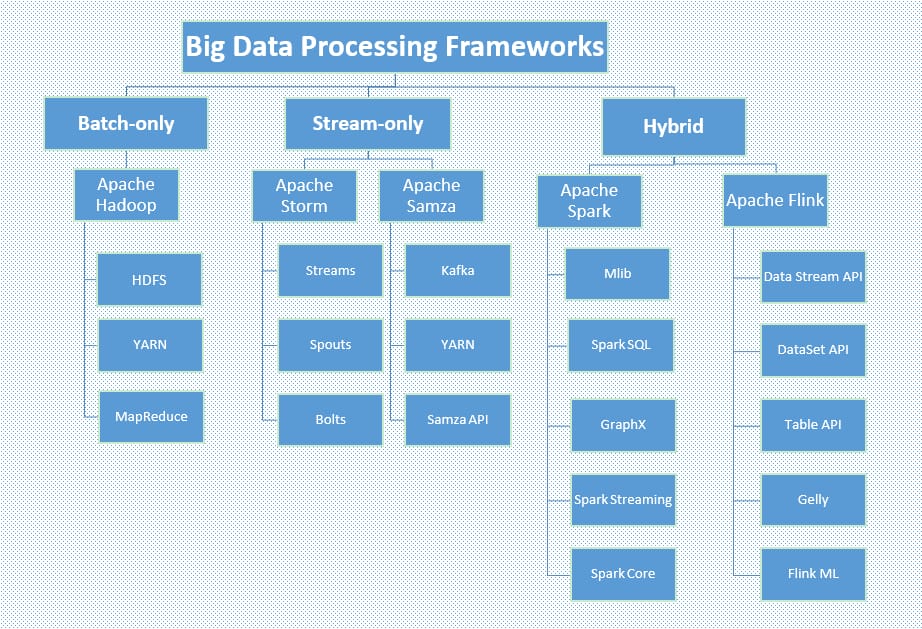
Big data frameworks classified by data analysis type, Source: Octoparse
Hadoop ecosystem. The most popular big data framework for batch workloads, Hadoop isn’t time-sensitive, which makes it less expensive to implement than others. Its ecosystem includes such tools as HDFS, a Java-based distributed file system; MapReduce, a framework for writing applications that process the data stored in HDFS; YARN, a workload managing and monitoring operating system; Pig and Hive querying tools; and HBase NoSQL database.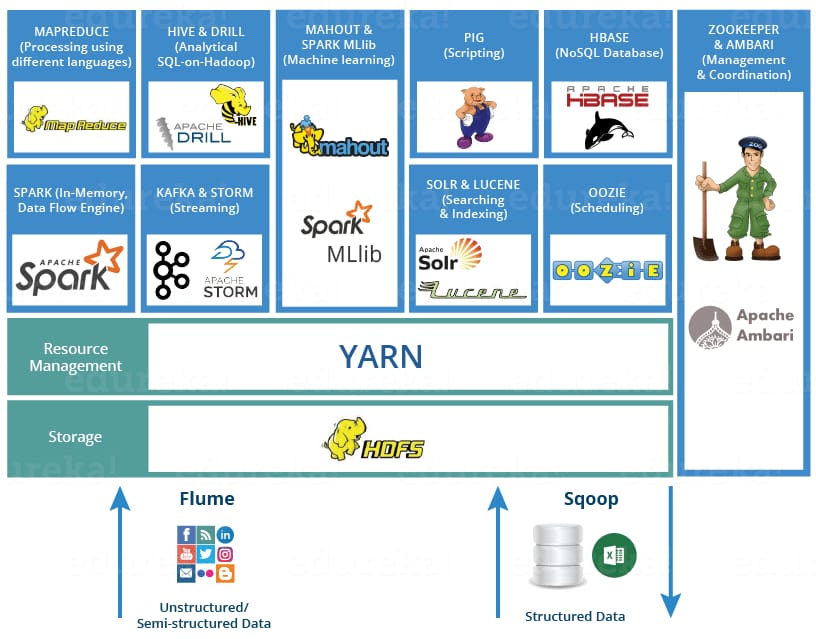
Big data frameworks mapped out, Source: Shubham Sinha
Real-time processing frameworks. Kafka is a stream processor that big data engineers use for running concurrent processing and rapidly moving large chunks of data. However, integrated with Hadoop, Kafka can also perform batch processing of the stored data. But more commonly, it’s used with real-time processing frameworks Spark, Storm, and Flink. For mixed workloads requiring higher speed batch processing and micro-batch processing for streams, big data engineers use Spark. In addition, its growing library of algorithms makes Spark a go-to big data ML tool.
NoSQL technologies
Along with big data frameworks, big data engineers use NoSQL databases to handle, transform, and manage big data. Having quick iteration and Agile structure, NoSQL databases enable storing large volumes of unstructured data.
HBase. A column-oriented NoSQL database, HBase is built on top of HDFS and is a good match for scalable and distributed big data stores.
Cassandra. Another highly scalable database, Cassandra has a major pro of requiring minimal administration.
MongoDB. A document-oriented NoSQL database, MongoDB is schema-free allowing schemas to evolve as the application grows.
Big data Machine Learning toolkit
Along with SparkML, the following tools help big data engineers integrate Machine Learning in their big data infrastructure.
H2O. This is an end-to-end solution for gathering data, building models, and serving predictions. It works with Hadoop and Spark frameworks and includes such development environments as Python, Java, Scala, and R.
Mahout. It allows for scalable machine learning on big data frameworks. Tied to Hadoop, Mahout also runs as-is outside of it enabling stand-alone applications to migrate into Hadoop and vice versa - Hadoop projects can span off into their own stand-alone applications.
When to hire a big data engineer?
Most probably you need a big data engineer, if your business is in one of the following industries:
Internet of Things. IoT companies require fast data ingestion because they’ve got many devices sending in data non-stop. A big data engineer will carefully set up the data flow making sure no important information is lost.
Finance. Having all sorts of input data for processing, financial organizations have very specific
big data needs that require a great deal of domain knowledge. That’s why in your case it could be more efficient to train the existing staff on big data because they already know the systems.
Social. Making wise use of users’ data, social media companies understand who their customers are and what they like so that they can skillfully market products to them. Social media leverage the cutting edge technologies or even create their own big data solutions, e.g. Presto from Facebook and Apache Storm from Twitter.
Marketing and eCommerce. Tracking every online interaction of users with their site, marketing and eCommerce companies collect vast quantities of data about their customers.
Also considering that this information is spread on hundreds of web servers’ log files and on many different systems, big data engineers have a lot of work to do here.
Government and Non-profits. All parts of government use big data and it comes in different flavors. Big data engineers will establish data processing where datasets will be joined together to process them at once for the most valuable insights.
If your industry isn’t on this list but you’ve got a lot of customers, this means you have data coming from many different sources. You can definitely make use of big data solutions to combine all of the material in a single place so the customer service representatives have a complete view of the customer. As a result, you’ll be able to act upon this information to improve your customer care.

