To find bugs and logical mistakes in the software, it is essential to engage in quality assurance activities. However, QA testing won’t tell you if the product is aligned with business objectives and can perform required tasks in real-world scenarios. So, to verify the development team is building the right solution for the actual end users, conducting user acceptance testing is vital.


User acceptance testing explained
What is user acceptance testing and how is it different from quality assurance?
User acceptance testing (UAT) checks whether a product is right for end users. The word testing makes many people think it’s the same as QA, but that’s not exactly correct. Let’s see what these and other related terms mean and how they are different.
UAT vs QA
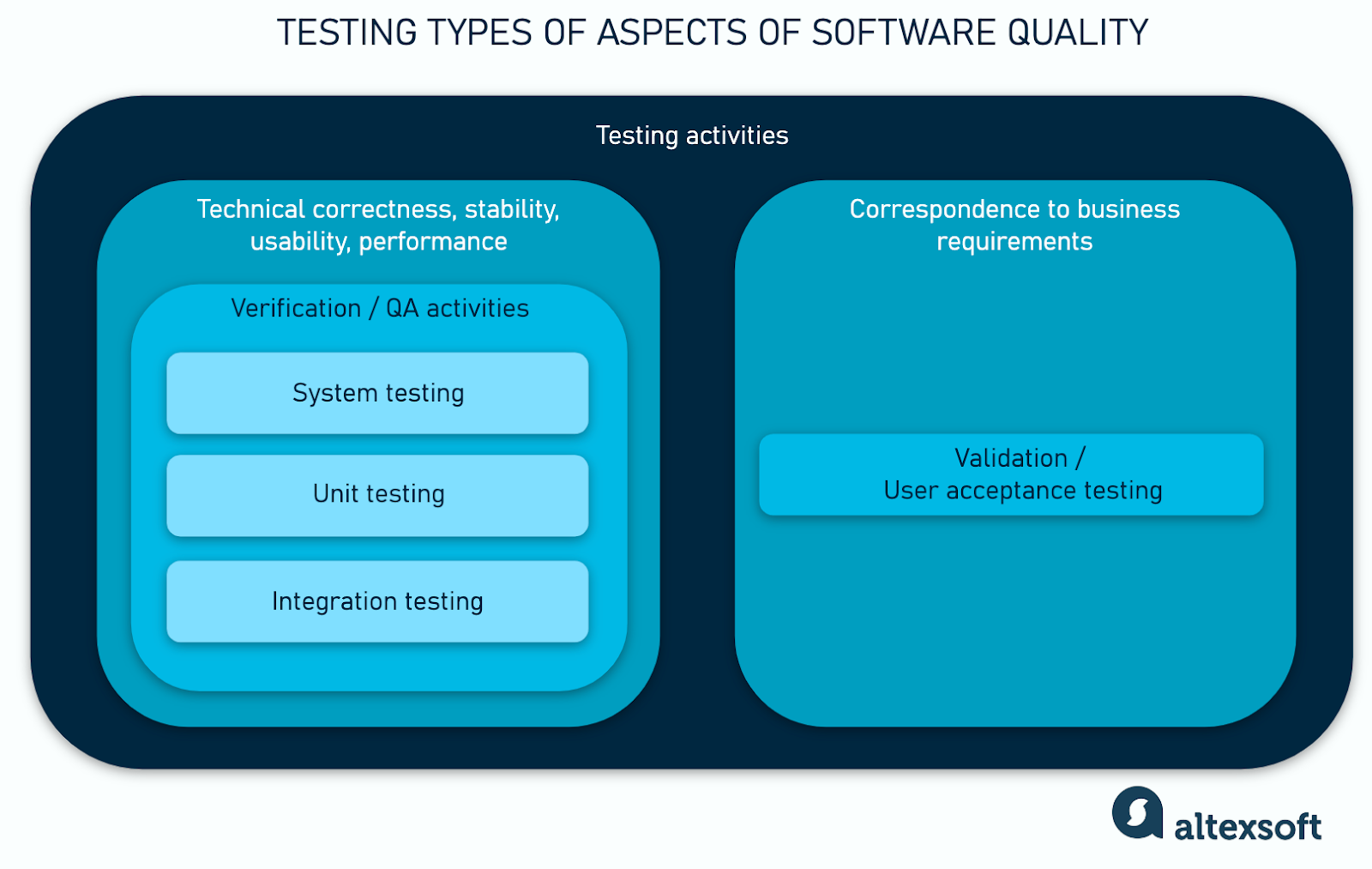
In the testing process, it’s important to distinguish between validation and verification.
Verification refers to general QA processes aimed at checking technical aspects of a product to ensure it actually works. It is carried out by QA engineers and testers throughout the development process. Their goal is to identify and fix bugs, test functionality, check performance, and validate security and integration. QA is based on technical specifications, and defects are reported to developers for resolution. The QA team decides when the software is stable enough to move forward. Read more about Quality Assurance in our whitepaper.
Validation is a different name for UAT, and is conducted to confirm that the product corresponds with business requirements and meets the needs of the end user. It is performed by end users, business stakeholders, or product owners to ensure the software meets real-world business needs. Instead of focusing on technical correctness, UAT validates whether the software works as expected in real-life scenarios. If any issues arise, they are reported to business decision-makers, who determine whether the product is ready for release.
Validation and verification activities in terms of overall product testing
In summary, QA ensures the product is functional and bug-free, while UAT ensures it is usable and meets business objectives. Both are necessary to deliver high-quality software that satisfies users.
UAT vs SIT
SIT (system integration testing) and UAT both happen late in software testing, but serve different purposes and are performed by different teams.
SIT happens first to ensure that different system components or modules work together as expected. Developers or QA testers conduct it to identify defects in data flows and interactions between individual elements or modules — APIs, databases, frontend, etc. For example, SIT can include testing if a payment gateway integrates correctly with an e-commerce website. UAT is conducted after SIT to ensure the software meets business requirements and is ready for end-users.
Some SIT and UAT test cases might look similar (e.g., verifying a feature works), but their perspective differs. For example, in SIT, testers check if a login interface properly communicates with a database; In UAT, users check if the login process follows the expected flow.
Both testing stages use environments similar to production, so people assume they serve the same purpose. However, SIT is more controlled, while UAT mimics real-world usage.
For more info on how system integration works, check out our article.
UAT testers: Who performs UAT?
UAT can be performed by
- the actual users of an existing product,
- users of a previous version of a product,
- stakeholders involved in the development of the product, and/or
- business analysts as end-user specialists.
This enables the development team to fix most of the usability problems, bugs, and unexpected issues concerning functionality, system design, business requirements, etc.
Why do you actually need UAT?
The main purpose of acceptance testing is to validate that the product corresponds with the user needs (defined at the product discovery stage) and is ready for launch. According to an Origsoft survey on UAT usage, over 75 percent of respondents said they conduct multiple cycles of end-user testing with 57 percent claiming the poor quality of the product as a cause.
So, here are the main reasons why UAT is important and should be a part of your development.
Ensure correspondence with business requirements. As we already mentioned, UAT is done to verify that the product operates in the real-world circumstances as required and allows end users to solve targeted problems. If you skip UAT, you might miss out on some critical flaws or system malfunctions that will inevitably cause user dissatisfaction.
Adjust initial requirements. Sometimes, as end users test the product, they can come up with valuable thoughts on how to improve the tested software. Getting such feedback will allow you to adjust your requirements and get a better result for your customers.
Avoid losses. First, UAT will allow your team to improve the product cheaper and much more easily (that mostly concerns the Agile model though). Second, we all know stories about product failures because of poor functionality and usability. UAT provides you with real-world user feedback and makes it far less likely to have losses caused by an unsuccessful product launch.
In any case, UAT requires organization and preparation work to make it effective. If you want to ensure your product’s validity, consider the following steps in conducting user acceptance testing.
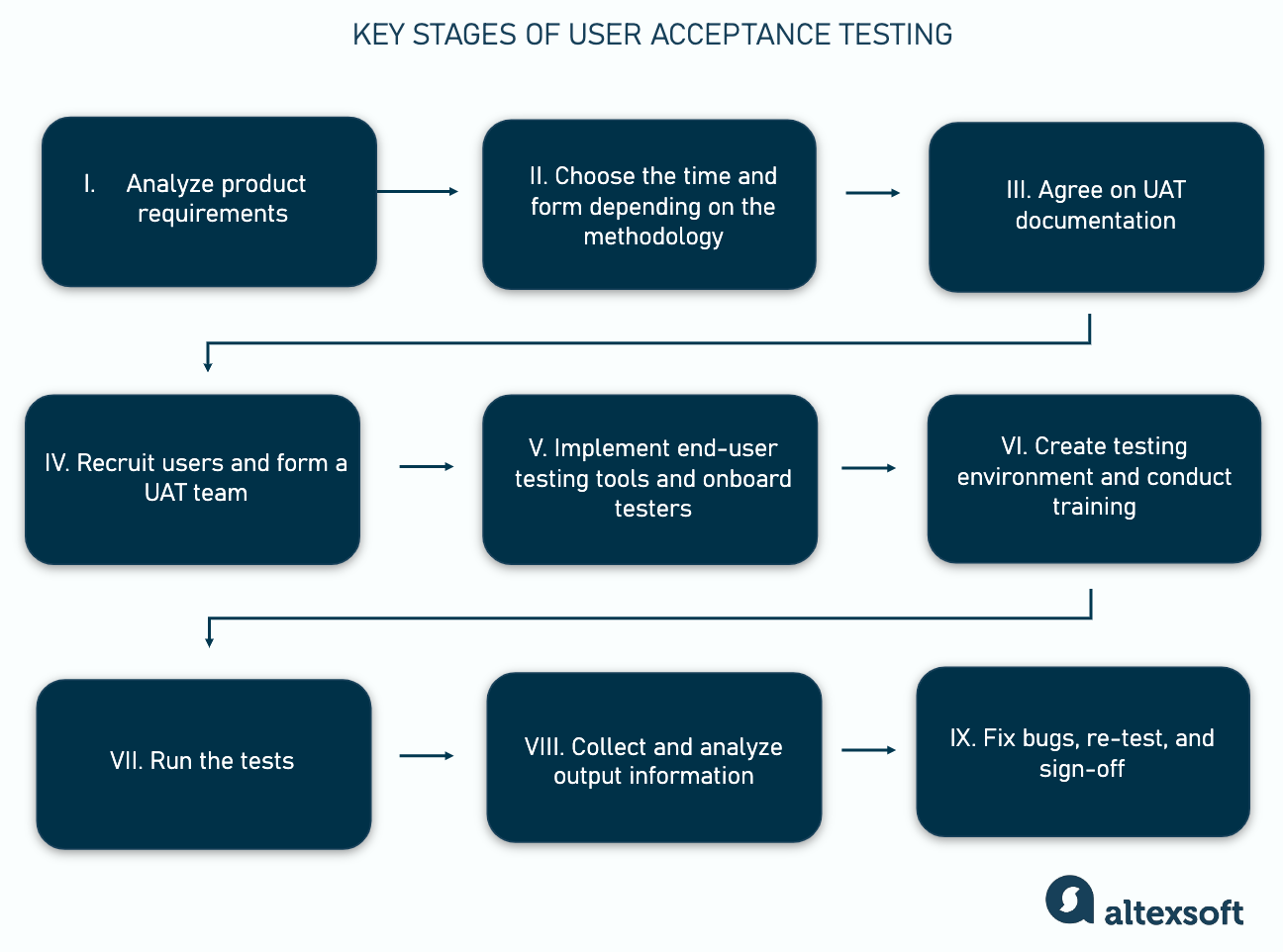
UAT key stages
1. Analyze product requirements
Analyzing product requirements is the first step of UAT planning. The primary source of input information would be the software requirements specification as it includes the complete scope of business and functional requirements.
Business requirements are high-level objectives of your organization that communicate business needs. For example,“customers should be able to use multiple payment methods.”


Learn more about documenting business requirements
Functional requirements bridge a technical solution with the business requirements. So, a functional requirement might sound like “implement PayPal, Visa, Mastercard, and Payoneer acceptance at checkout.”
The overview of these requirements will tell you exactly what you should test, whether the implemented solutions work for the users and solve problems for the business. Functional requirements can be translated into test cases, considering the success criteria of business requirements. And that will help you form an overall testing strategy. Consider engaging your business analysts, QA engineers, or product owners for requirement analysis.
2. Choose the time and form of end-user testing
Acceptance testing may take place at different stages of the project, depending on the methodology you are using, but typically it’s conducted at the end of the development cycle before release. As two most popular project management methodologies in software development are Waterfall and Agile, we will look at the user acceptance testing process within those models.
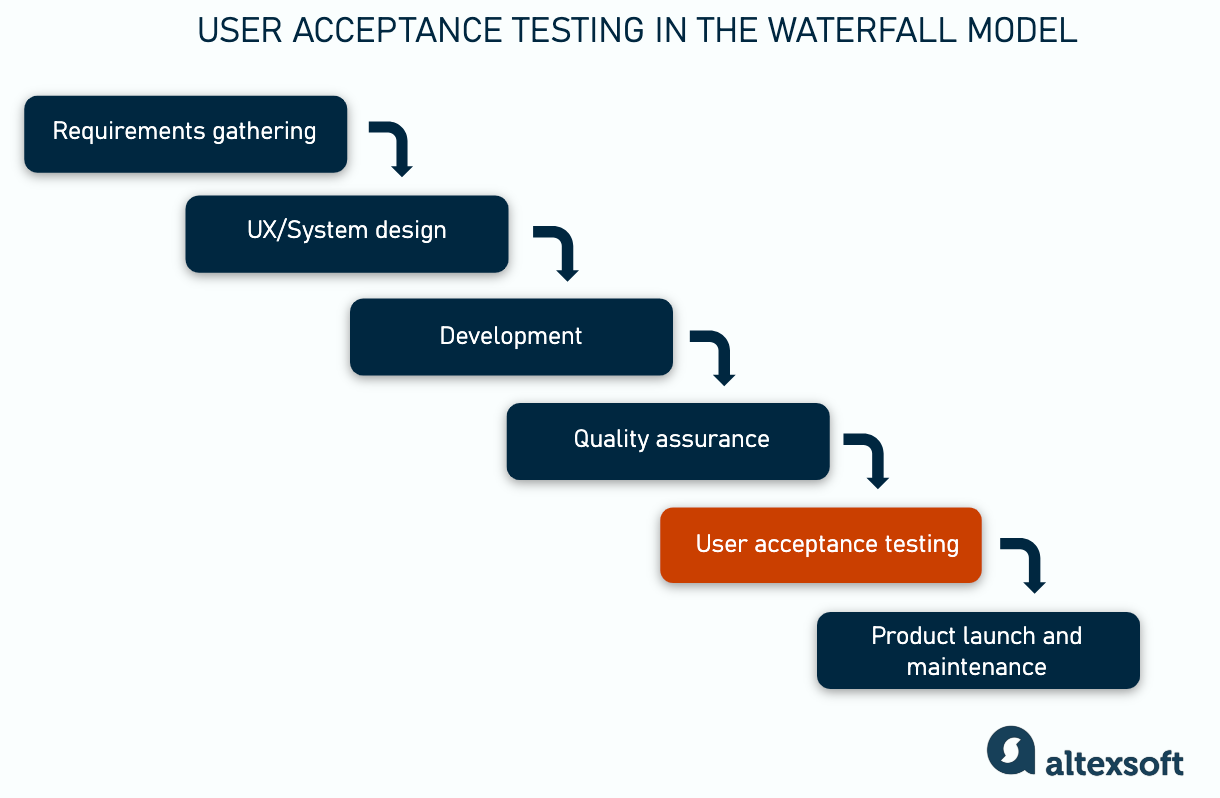
Acceptance testing in the Waterfall model
A Waterfall model is a traditional project management methodology based on a step-by-step development of the product.
The stages don’t intersect, meaning there is no simultaneous designing and design testing, or development and testing. The whole process is strictly documented and intended to deliver a fully functional application at the end of development without iterations.
User acceptance stage within the Waterfall model
User acceptance testing in Waterfall takes place at the final stage of development, right before the launch.
It can be conducted only after the system is considered code and function ready, after achieving the following benchmarks.
- Product business requirements have been met.
- The code base is finished.
- QA activities (system, integration, unit testing) have been completed.
- Bugs revealed during the QA stage have been fixed.
- Minor visual issues are in an acceptable range.
- User acceptance environment (UAT manager, tools for testing, test scenarios, etc.) is created.
In the Waterfall model, user acceptance testing is the definitive point that demonstrates software readiness. If a product meets user acceptance criteria, it means the product is ready for production. UAT activities, in that case, are for completing the system check, including its functionality, usability, and bugs. But still, the primary goal is to ensure that the product corresponds with the initial requirements and end-user needs.
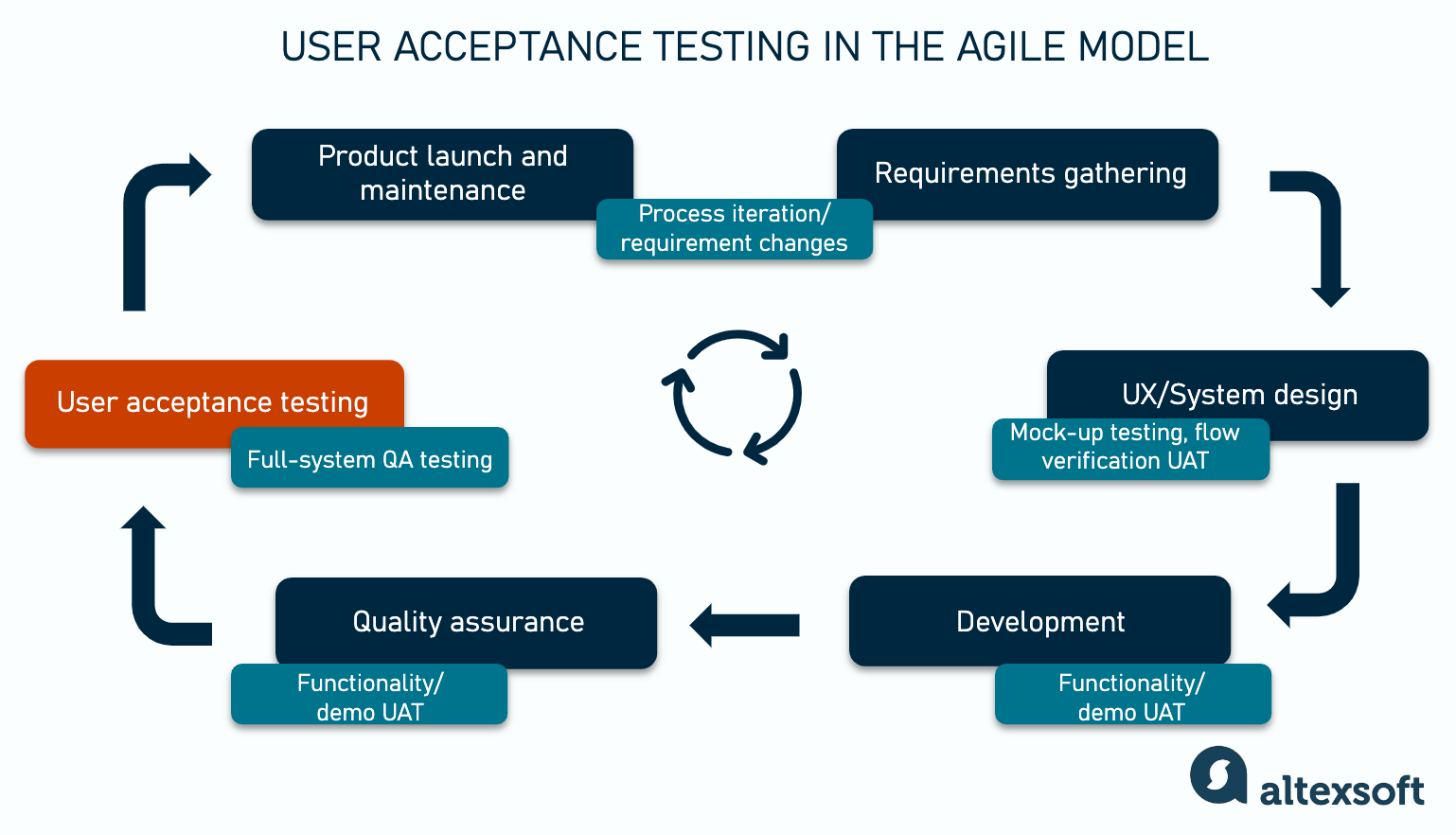
User acceptance in the Agile methodology
Agile project management isn’t as straightforward as Waterfall. It’s based on iterating each development stage until the product reaches the required quality and functionality. Iterations allow for dynamic change in requirements, as Agile doesn’t focus on creating much documentation. And that, in turn, enables engineers to quickly respond to customer feedback.
User acceptance testing in Agile model
The image shows the Agile product development cycle with iterations. The main difference between UAT in Waterfall and in Agile is that UAT is carried out multiple times (often within each stage) and its results may impact the initial requirements, as it delivers instant feedback on what works the best.
The checkpoints for starting end-user testing in an Agile project are
- formed business requirements,
- UX/system documentation,
- testing material (interactive mock-ups, high-fidelity prototypes, demos), and
- user acceptance environment.
In Agile, UAT is an integral part of overall testing activities, so it may take different forms and use different tools. For example, these can be tests on functional and non-functional requirements or early-stage testing to validate assumptions made during the planning stage. At the end of each iteration, acceptance testing produces deliverables that are used to modify requirements, system architecture, UX style guides, etc.
3. Agree on UAT documentation: UAT plan, UAT test cases, and more
Before starting user acceptance testing, it’s essential to establish clear documentation to ensure alignment between all stakeholders. Well-structured UAT documents provide a roadmap for the testing process, defining objectives, responsibilities, and expectations.
Below are the key documents that should be created for UAT.
UAT plan. Creating a UAT test plan will help you keep everybody aligned with the same objectives and vision. Being the main document, it includes all the information concerning what will be tested, by whom, and how. To cover all the organizational and processual aspects of UAT, you have to detail the testing strategy and entry/exit criteria.
End-user testing strategy. Your testing strategy should cover
- product description,
- testing objectives,
- testing scope,
- standards,
- testing types,
- testers/roles,
- process curators (managers),
- reviewers,
- reporting standards, and
- outcomes.
Entry criteria. These are the conditions that establish the software readiness to be tested. They are set at the earliest stage of planning by the development team, QA, business analysts, and stakeholders.
Exit or acceptance criteria. These are the conditions dictating that the software is valid for users. Matching acceptance criteria would be the final stage of your UAT.


Acceptance criteria explained
Test scenarios and test scripts. Test scenarios are hypothetical situations that users may encounter when interacting with your product, while test scripts are formal, detailed descriptions of the actions needed to perform UAT. Their aim is to guide your testers through possible system usage problems.
Basically, a test scenario should convey a simple idea of what will be tested. An example of a scenario is “check shopping cart functionality.” Each user scenario is connected with one or two requirements or user stories. They are written to validate that the system is usable, checking the end-to-end operations with real data.
Test scripts often contain a sequence of specific steps to take. They give exact instructions on what testers should do, as well as describe expected results. For example, a script can suggest clicking the “Ok” button that has to be followed by a confirmation popup.
To write good test scripts and scenarios for user acceptance testing, consider involving end users in approval to include all the possible use cases, both common and uncommon. Also, consider writing them in plain language, avoiding complicated phrasing or overly techy explanations.
Test cases. A test case is a set of specific actions that are taken to test and verify a particular system behavior, feature, or functionality. Test cases are more detailed units that have to correspond with all the test scenarios. Most often you will rely on your user stories and business use cases to write efficient test cases. Examples are:
- Check an unregistered user adding the product to the shopping cart.
- Check shopping cart filtering.
- Check the “continue shopping” button.
Test cases are efficient when there is a clear purpose stated, and users are able to understand what they should do to complete it. The user guide to a test case may look like this:
- Open the application.
- Add any product to a shopping cart.
- Authentication is not needed.
- Proceed to the shopping cart.
You may also include expected results in the test case so that the user is aware of what is going to happen:
- The product will appear in a shopping cart.
- The system will ask you to authorize as a registered user.
4. Recruit users and form UAT team
As we mentioned earlier, testers can be recruited from your existing user base. Depending on the project specifics, those can be subject matter experts, real-world users of the product, stakeholders, business analysts, or a product owner. You can also use crowd-sourcing platforms to search for testers or hire a freelance specialist.
Consider creating a social media message or even a landing page to attract an audience. Your potential testers should not necessarily be tech-savvy or familiar with software testing processes. However, the ones who already have or will use your product (or maybe a similar one) will be good candidates for your UAT since in that case you can avoid deep onboarding and QA team involvement.
5. Implement end-user testing tools and onboard testers
There are specific instruments on the market that are designed for end-user testing. Most popular tools offer testing management functionality like reporting, task overviews, and testing documentation templates. Here are some examples of software that can be used to support your UAT activities.
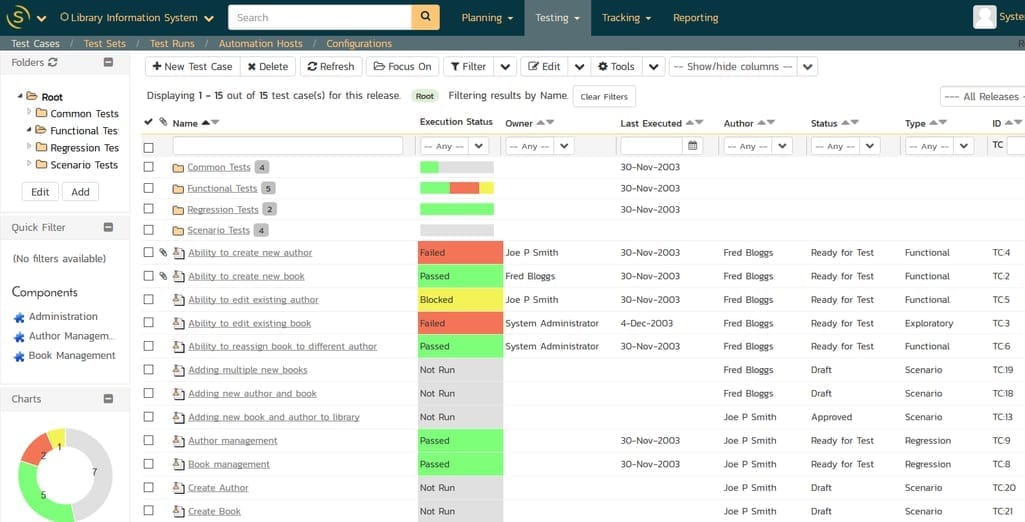
Testing dashboard in SpiraTest
Usersnap is a popular platform that allows users to mark bugs right on the screen, leave comments and suggestions, and share feedback. There are a lot of similar instruments such as Userback and UserTesting.
FitNesse is an open source, wiki-powered framework for acceptance test automation. It allows all stakeholders to easily create, edit, and run tests, leaving early feedback. Users enter specially formatted inputs to automatically generate tests that are immediately executed by the system. Then the output is returned and highlighted depending on whether it matches the expected result or not. This collaboration platform has a mild learning curve and is popular among Agile teams.
Bugwolf is another instrument for conducting UAT. Besides testing environment and bug reporting, it offers gamification and competition features to motivate and engage users. You will also find built-in payment options if you are going to conduct end-user testing online.
Well-known project management tools like Jira or Trello also have functionality for performing UAT.
6. Create user acceptance environment and run training
To get the most out of end-user testing, start with the training. Your testers and UAT manager are responsible for that. Consider structuring your training process to include the following aspects.
- Introduce users to the testing process, its objectives, and tools.
- Provide them with reporting standards and guidelines.
- Ensure users understand test cases properly, providing support if needed.
- Give them access to the testing environment.
Most often end-user testing can be done on the user's side and online, meaning you won’t have to supply your testers with the hardware. More complicated projects or confidential data may require gathering a dedicated team of user testers at your office. It’s also important to appoint a manager who will provide documentation, tools, and support.
7. Run the tests
Once you have your test scenarios and test cases, you are good to go with the tests. To support your end users during the process and get the required results, ensure that users have a clear understanding of what actions each test case requires. Keep in mind that theyare not professional testers. During the test, provide real or close to real data to the users, avoiding sample content or dummy buttons. Any misconception may get them stuck at the test case.
Another important aspect is having your developers ready to fix anything that goes wrong. Your testing environment can shut down or there can be errors preventing users from testing. They should be able to access required functionality at each stage of testing, whether it’s an interactive design or a functional app, to perform each test case included in the test plan.
8. Collect output information and analyze it
During your UAT activities, you will get tons of data from testers. Your QA team will have to analyze it. The data is collected via user reports submitted manually or via a specific tool. Additionally, you can conduct interviews with separate users to get more insight into the test cases they performed and what they think of them.
To evaluate system readiness, consider measuring the percentage of tests passed/failed/fixed.

Test tracking dashboard in Panaya
There are also a few more points that should be considered.
System stability. Stability can be determined by the number of unexpected errors met during the UAT.
Testing coverage. Coverage is measured by the number of test scenarios/cases written and their ratio to the overall finished tests. You may also match your UAT testing results with the customer journey map to understand which part of functionality was left unchecked.
System usability. This can be calculated by the number of tests not passed because the user didn’t find a way to do it. But the overall UX is tested during usability testing, which is conducted as a separate activity.
Contract/requirement compliance. Requirement compliance is checked after all the end-user tests are finished. It ensures that the software corresponds to the initial requirements/contract scope, even after changes brought by user acceptance.
9. Fix bugs, retest, and sign-off
After executing UAT, all defects must be documented with relevant comments and passed to the development team. They, in turn, must make adjustments to the code to address the issues revealed by UAT.
Once you fix the bugs, retest them to make sure everything is working properly. When the acceptance criteria are reached and approved by reviewers, the final acceptance decision is made about production readiness of the product.
UAT team roles
As we mentioned earlier, UAT testing is different from other QA activities because it’s performed not only by tech specialists. It’s important to engage actual end users in this process. Involving QA professionals and business analysts is also necessary, as is close collaboration with the project manager and development team.
The responsibilities of the UAT team can differ depending on the company and project needs, but here is an example of the role distribution you can consider.
Business program manager. This is the person that coordinates and oversees the entire project, aligning it with business objectives. Before the UAT stage, the program manager should generate a program delivery plan and business requirements document to support testing activities. He/she is also responsible for reviewing and approving the test plan and test strategy.
During UAT, the program manager monitors test activities execution and ensures completion on schedule and budget. Afterwards, he/she reviews the test report and decides on deployment to production.
UAT test lead/manager. The test lead's responsibility is to accurately plan and organize UAT. For that, close cooperation with the project manager is required.
The test lead gathers and analyzes all the business and functional requirements, which are then used to develop the necessary documentation, i.e., test strategy, test plan, test scenarios, etc. Additionally, at the preparation stage, he/she works with the test team, assigning test scenarios to team members and organizing training to make sure testers understand the UAT procedure. The test lead also prepares and manages necessary resources and loads essential test data in test tools.
Throughout the UAT, the lead coordinates the execution of test cases, making sure all test results are documented. He/she also tracks test progress, collects metrics, and creates/maintains a test report.
UAT test team members. The main task of the test team is to execute tests in accordance with the provided schedule and instructions. Testers should create test logs and report on defects and incidents. They also typically participate in retesting activities (if needed).
The project manager, as the person responsible for successful project completion, has to monitor testing activities, provide organizational support, and report on progress. He/she would also act as a mediator between the testing team, developers, customers, and any other possible stakeholders.
User acceptance testing checklist
Summing up the UAT guidelines we presented above, we’ve developed a checklist to help you organize your testing activities and not miss out on anything important.
Initiating the UAT project.
- Verify with your development team that all product components are ready for testing. Document any issues that could not be addressed before the UAT.
- Identify key stakeholders.
- Choose a team leader responsible for the project, including paperwork.
- Discuss and agree on the project structure, UAT team, and UAT documentation.
- Thoroughly discuss testing procedures and create an initial UAT plan.
Planning UAT.
- Create your UAT team and make sure you have testers from each market segment and/or each group of stakeholders. Be certain all participation-related documentation is complete and signed (nondisclosure, participation agreement, etc.).
- Communicate the testing strategy and schedule to the team. Make sure every member understands roles, procedures, and responsibilities.
- Make sure all business requirements are captured and communicated to the UAT team.
- Discuss and agree on entry and exit criteria.
- Prepare all the business documentation: test plan, test scenarios, test cases, etc.
- Communicate business objectives and acceptance/exit criteria of the system.
- Agree on reporting standards.
- Conduct the needed training on the system and auxiliary tools. Make sure testers understand how to report incidents.
- Gather and prepare all the necessary resources for UAT activities. Book space if needed.
- Prepare and test the environment, test management tools, devices, servers, feedback channels, issue tracking, content delivery, etc.
- Make sure you have all the logins, security access has been set up, and test data has been loaded.
Executing UAT.
- Monitor how procedures are carried out and make sure reports are submitted timely and accurately.
- Create and maintain a test summary report.
Post-UAT activities.
- Analyze output information by measuring the percentage of tests that passed/failed as well as categorizing defects by severity.
- Identify status against acceptance criteria.
- Prepare a final UAT report and present it to stakeholders together with the estimated time and effort required to meet acceptance criteria and recommendations for release.
Testing procedures might differ from company to company. Here are a couple of other downloadable UAT checklists that might fit your needs as well: Checklist 1, Checklist 2.
User acceptance testing templates and examples
We’ve mentioned a few important documents that have to be created for proper UAT planning and execution. There are different ways to write them, but we offer some templates that may come in handy.
Test plan examples
A UAT test plan outlines the overall strategy, scope, objectives, and roles for user acceptance testing.
Template Structure:
- Introduction
- Purpose of the UAT
- Scope (what features/processes are being tested)
- Assumptions and risks
2. Roles and Responsibilities
- Who will be involved (business users, testers, developers)
- Responsibilities of each team
3. Test Approach
- Entry and exit criteria
- Test scenarios and test cases
- Acceptance criteria
4. Test Environment & Data
- Description of the UAT environment
- Test data setup
5. Test Execution & Reporting
- How test results will be logged
- Defect tracking process
6. Sign-Off Process
- Who approves UAT completion
- Acceptance or rejection criteria
Luckily, you don’t have to create your test strategy and plan from scratch. There are plenty of templates available that you can download and customize to suit your test project.
- UATest Plan template by SDLCforms,
- Test Plan template by Coley Consulting,
- iiba template (downloadable link),
- Test plan example by QATestLab,
- Test plan outline based on IEEE 829-2008
- Test plan template by IBM
Test scenario and test case examples
A test scenario is a broad test case that describes a feature or function to be tested.
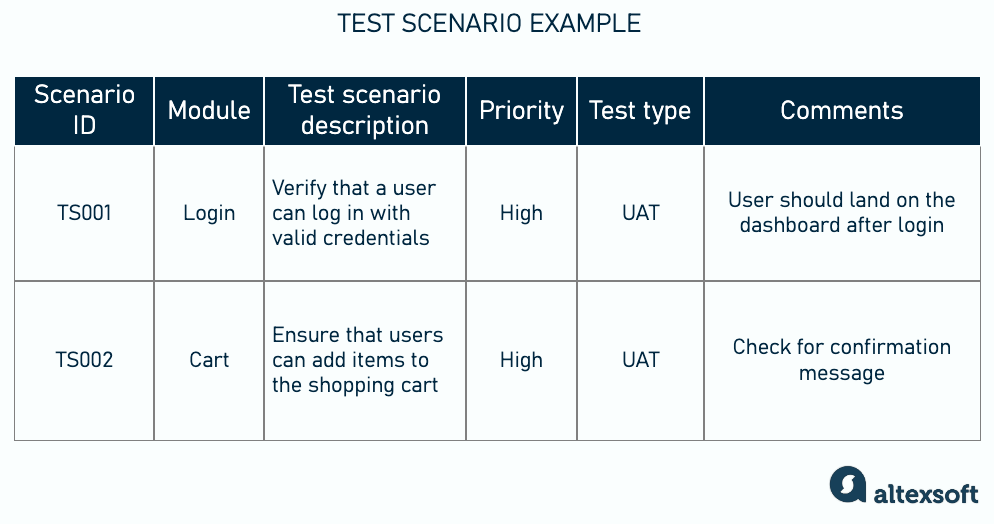
Test scenario example
A UAT test case document outlines specific test scenarios, steps, expected results, and actual outcomes.
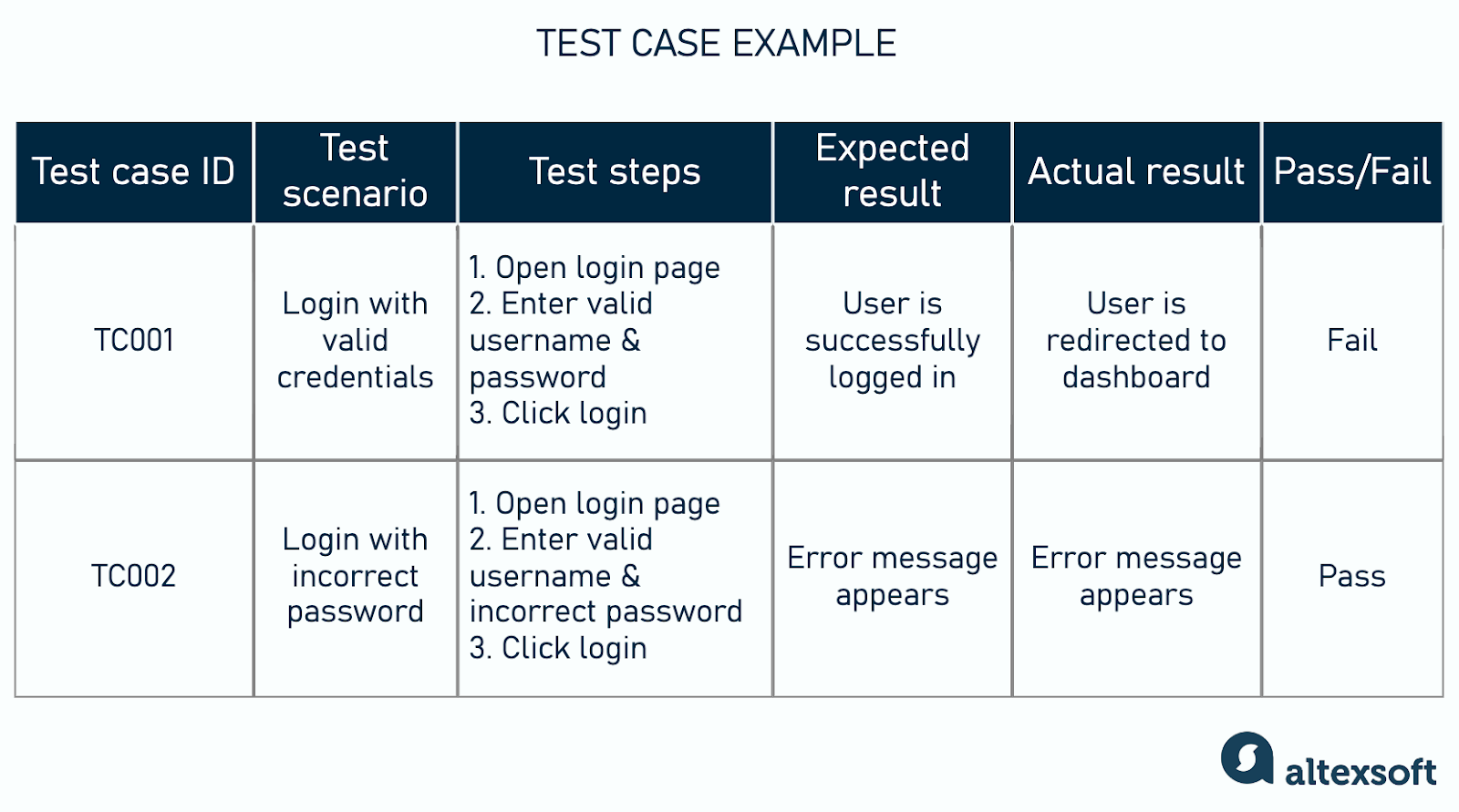
Test case example
Here are some sources where you can download
- Test scenario templates by StrongQA
- Test script template (downloadable link) and test script example
- Templates by Smartsheet
- Templates by TestRail
- Templates by TemplateLAB
Test report examples
A test report summarizes test execution, defects found, and whether the software is ready for release. Below are templates and examples for creating structured test reports for UAT, system testing, or regression testing.
Template Structure:
1. Test Report Overview
- Project Name:
- Test Report Date:
- Tested By:
- Test Environment:
- Testing Type: (UAT, Functional, Regression, etc.)
2. Test Summary
- Total test cases: 50
- Passed: 40
- Failed: 5
- Blocked: 5
- In progress: 2
3. Defect summary
- Defect ID: BUG-101
- Module: Login
- Severity: High
- Status: Open
- Description: Users unable to log in with the correct credentials
4. Test Findings & Recommendations
- Major issues that need fixing before release.
- Any recommendations (e.g., retesting required, additional UAT needed).
5. Sign-Off
- Approved By:
- Date:
- Decision: (Go/No-Go)
You can get more report templates here:
- Test report template by QATestLab
- Test report templates by StrongQA
- Test report by ClickUp
UAT challenges
Just like at any other stage of the development cycle, certain challenges might arise during UAT activities. Here are some of them – together with ideas on how to be prepared:
- poor planning – sufficient time has to be scheduled for UAT, otherwise the results will be incomplete;
- wrong testing environment – for UAT, the environment should be different from the one used for functional testing;
- inappropriate tester selection – testers have to be chosen from the corresponding consumer group which is the main target audience of the product;
- lack of training – testers have to be well-trained prior to conducting UAT, otherwise it won’t be effective; and
- inefficient communication – a seamless communication process between teams has to be set up to avoid gaps, misunderstandings, and delays.
Keeping these challenges and our guidelines in mind, you’ll be able to conduct efficient and productive user acceptance testing.

