Native or Cross-Platform Mobile Development?
As the world is getting rapidly digitalized and global mobile data traffic grows extremely fast (by 69 percent as of 2014), the question is not about the need to create a multiplatform app, but rather which programming tools and methods to use. Android and iOS continue to be the most supported mobile platforms, while WP8 is the platform that tops the users’ wish list. According to the data provided by comScore, Android hovers at around 52 percent market penetration, the iPhone has a 42 percent share and Windows Phones own 3 percent of the market. When considering your mobile development options, make sure you take into account all three of the major platforms for your app to run on.
The choice you will have to make regarding you app is whether to engineer it natively or use cross-platform mobile development tools. If you do decide to write separate versions of your app on each platform, your app will get truly native interfaces and great hardware-related features. Yet, you will waste time replicating the app and spend a lot of money on development and support.
Assuming you write the app in a single codebase and drop it into a “magic box” tool, the user experience and performance output is likely to be extremely poor.
The third option would be using Xamarin as your cross-platform development tool. Its ultimate benefit is delivering native experiences while reducing costs and time to market. Anyhow, let us go through all the pros and cons of all the options together.
Native Mobile Development as It Is
What you need when creating a native app, is people having deep expertise with the language and API. Native mobile development results in truly native experiences that take the most benefit out of a given platform. Thus, once you decide to provide your business with a digital presence, you start leaning towards this exact option and quickly make the obvious choice in its favor. Indeed, native environments are the best fit for a number of applications. These are the cases when it’s preferable to engineer a native mobile application:
- When developing mobile solutions based on video or game scenarios or apps with visually loaded design, navigation, and animations
- When integrating hardware-related features, such as gestures, multitouch events, geolocation tracking etc.
- When developing utilities that manage system resources or Operating Systems (OS)
- When the solution requires processing large amounts of data on the client side
However, odds are that native development might become the most expensive option for you. The main reason for it would be the quite limited code reusability. While building exclusive apps on the three major platforms such as iOS, Android and Windows, you staff three separate teams with different sets of expertise; engineer all the features in different ways and then fix quite a variety of different bugs. In addition, if you suddenly feel the market needs you to replicate the app on another platform, like Blackberry 10, you will have to start by writing specification requirements, gathering a team, and going through the entire development cycle all over again.
Likewise, the challenge arises when your app requires some additional changes or enhancements. You have to mobilize all the teams in order to complete a simple task like editing a text or modifying a button color, which is really quite wasteful. As a smart business owner or CTO, you would avoid all the time-consuming and cost-ineffective efforts. This is where crossplatform development tools enter the picture.
The 'Write Once Run Anywhere' Approach
Walking down this path of reasoning, the next turn you see is incredibly tempting: why not use of "write once, run anywhere” approach with tools like PhoneGap, Titanium, and Sencha Touch? The promise is about running on any operating system, of making the underlying code of the computer irrelevant. So you organize a single team to write a single piece of code, put it into “the magic box” adapting the app to the operating system and form factor of each supported device. Finally, the app runs across all the types of the devices. What could be more simple?
Yet, it is not as good as it sounds. What you need is to take seriously users’ expectations and preferences. For instance, iOS users are used to a tab bar for navigation at the bottom of the screen, whereas Android users mostly use a side drawer in their apps. To enable the corresponding experiences for your users on each platform, applying a completely cross-platform development approach is simply no good.
As Xamarin chief Nat Friedman says, “by definition it [WORA approach] results in a mediocre experience.”
The app you get at long last will have a number of platform-specific issues appearing here and there during use on desktops, smartphones, and tablets running on different operating systems. Both the user experience and performance will suffer, due to the limitation of each platform’s capabilities. Moreover, the framework’s vendor will take control over the app’s features from your enterprise. In the event the framework fails to adopt the app, it leaves your mobile strategy at risk.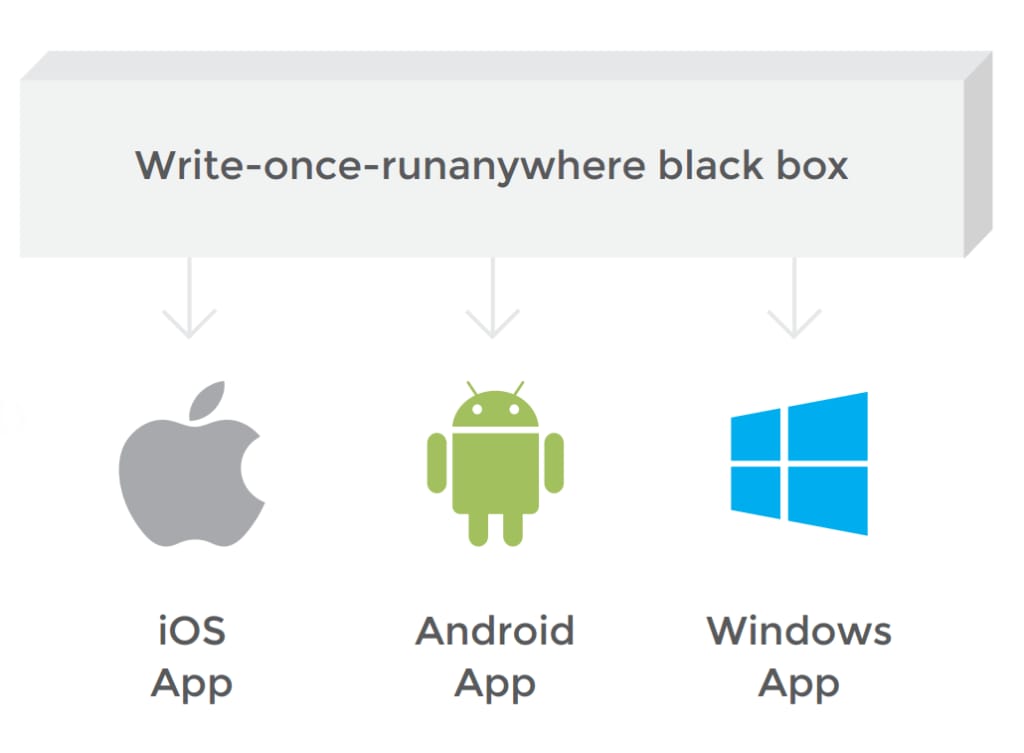
'You-Can-Have-It-All' Solution
The genuine compromise option would be using a development model which enables the advantages of the both extremes: Time-optimized and cost-saving code sharing and reuse, while at the same time, a rich performance, regardless of the device it's used on. Xamarin is just the right mobile development platform for answering these challenges. Here is why.
The Xamarin mobile development platform combines flexibility in code reusing in addition to advantageous native experiences. The platform lets engineers integrate the core logic of your app in a portable code layer used for all devices. It, in turn, becomes the foundation for building different native user interfaces for each operating system separately. Developers have access to the full spectrum of the platform functionality (e.g. iBeacons, Android Fragments) and make the best use of it all. As a result, the pages, layouts, and controls are fully-featured, whereas the app looks native across devices and performs accordingly.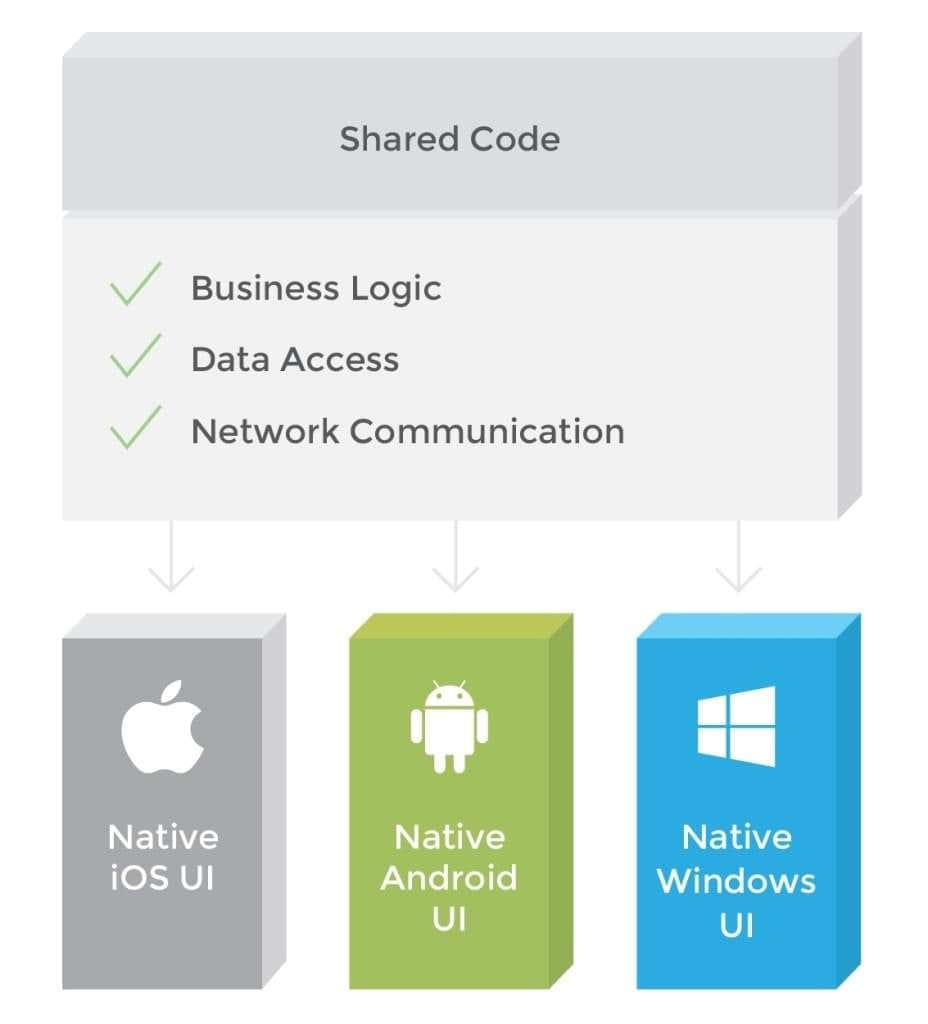
Due to effective allocation of resources, Xamarin development is timesaving and cost-effective. Your all expert team works on the project in the familiar API, knowing exactly how the app will work and behave in advance. The Xamarin controls are convenient, and help engineers enable a native functional product in a timely manner. Your team develops an app with much of the code reused, single toolset available and APIs unified. This cuts down the expenses on knowledge transferring, development framework configuration and deployment of the various app’s features. In other words, you get an attractive, well-performing app up and running faster and less expensive than building several different native apps.
Down to Details: What Is Xamarin and Why Use It
If you have not used Xamarin yet, you probably have not heard of it. According to the research2guidance’s Cross Platform Tool Benchmarking of 2014, low awareness is the main barrier for making use of this convenient cross-platform development tool. Let us get familiarized with its capabilities.
The .NET based Xamarin platform allows developers to use C# in creating various apps for desktop/PC’s, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs and even in-car devices. Since C# is a simple, contemporary, multipurpose object-oriented language, you can take great advantage of a strong typed language, lambdas, LINQ, and async programming.
Xamarin supports a number of operating systems, including iOS, Android, WP8, and Apple OS X. As an additional service, you can test your app on over 1000 mobile devices immediately in their Test Cloud which offers continuous integration, illustrative reports, test for fragmentation, and object-based UI testing. Moreover, you have an opportunity to analyze your app’s performance and users’ behavior through Xamarin Insights.
Once you get to know the Xamarin capabilities, the study says there is only a very small chance you will switch to its competitors. User satisfaction for Xamarin is very high: 75% of users are pleased with their pre-installed applications, access to device hardware features and Cloud API services. Currently, over 650,000 developers use Xamarin to engineer crucial enterprise and consumer mobile apps in a range of business verticals. The list of companies using Xamarin is quite impressive and lengthy. Have a look:
8 Ultimate Advantages of Xamarin
1. A Significant Reduction In Time To Market And Costs
You save an enormous amount of time and money by avoiding cross-platforms code duplication. That enables developers to do a number of programming tasks regarding database usage, network access, and business logic. Investing in a single team lets you manage financial resources more effectively. Of even greater appeal, your app gains the advantage of entering the market ahead of the competition. While your rivals are still fumbling about, managing three teams working separately on building native apps, your product is already conquering customers.
2. Overall Risk Mitigation And Lower TCO
As soon as you release the product, its market journey has begun. You will have to implement the app’s enhancements, feature updates and modify the app taking into account emerging technologies, which is quite costly in a number of ways. That is when Xamarin support will be of great value. Xamarin delivers new releases within two weeks of new device operating system features are available. Consequently, your app stays up-to-date at all times.
3. Wide Functionality Introduced Using Native APIs
Xamarin’s bindings equally correspond with those of native environments. If you request any native features for your app (e.g. GeoFence, accelerometer sensor, voice recording, push notifications), your development team can use native documentation to easily build them with C#. Additionally, your app gets the same visual appeal as in the development stage, so while creating the product you can be aware of how it will exactly look at the end.
4. Appealing Native User Interfaces
Having standard native UI controls on hand, developers are able to create a corresponding look & feel for the app’s pages, customized to the specific mobile platform. For example, engineers are able to use C# commands and refer to Apple’s CocoaTouch SDK frameworks and Google’s Android SDK as namespaces. Meanwhile, they can also get hold of Android Fragments, iBeacons, and similar platform-specific features. So Xamarin makes it easy for programmers to use C# syntax and access the platform-specific UI controls. Thanks to this helpful feature, your app gets rich native user experience and all of the wide-ranging functionality you require.
5. Robust Native Performance
Mobile apps built with the help of Xamarin perform natively because the tool leverages the platform-specific hardware acceleration. The C# code for iOS apps is ahead-of-time (AOT) compiled to assembly level ARM assembly language. The C# code for Android apps, in turn, is compiled to intermediate language (IL) and then packaged with MonoVM + JIT’ing. As for Windows Phone, you compile the C# code for it to IL and then it is executed by the runtime with no additional tools needed.
6. Greatest Possible Bug Elimination
With Xamarin, you can avoid introducing platform-specific errors due to the significant amount of shared code. Furthermore, the single programming language along with API allows developers to spend less time hunting and fixing bugs. Therefore, you save time for engineers to integrate additional sophisticated functionality and polish the user experience.
7. Extended Language Capabilities
C# has proven to be a considerably beneficial development language over the years. Its up-to-date patterns such as generics, LINQ, implicit typing, extension methods, async methods, and closures provide the basis for building clear and rock solid code. Meanwhile, your iterations can be implemented rapidly and safely, without any interruptions to the development process itself. If you do not need your app built from scratch, Xamarin also offers full integration with backend systems such as sales, inventory, customer service, supply chain, and CRM.
8. Simply Implemented Core Logic
Xamarin makes engineering an app for enterprises or customers easy and convenient. The availability of .NET and other C# Libraries (for instance, HTTPClient), supported by PCLS and Microsoft, along with the option to choose from the two integrated development environments (Visual Studio or Xamarin Studio) simplifies the job for developers. What you get in return is an almost limitless number of opportunities for creating complex apps to streamline business operations.
Conclusion
In light of the significant growth of the mobile digital market, your enterprise has to keep up with emerging technology trends and address the arising challenges. To achieve that, first of all your app should provide engaging and rich native experiences to your customers across platforms and devices. When it comes to actually implementing your idea into a beneficial app, consider all your mobile development options. Determine the full spectrum of features your app will require and plan the development process accordingly. Among others, Xamarin can become a crucially helpful tool for you to make the best of cross-platform mobile development.
References
- Top Strategic Predictions for 2018 and Beyond - http://www.gartner.com/technology/topics/trends.jsp
- Cross-Platform Tool Benchmarking 2014 - http://research2guidance.com/cross-platform-tool-benchmarking-2014/
- Smartphone Share Stabilizes in US, Competitive Only at Margins. Top Apps on comScore List Also Mostly Unchanged for More Than a Year. - http://marketingland.com/smartphone-share-stabilizes-in-us-competitive-only-at-margins-128138
- comScore Reports March 2015 U.S. Smartphone Subscriber Market Share - http://www.comscore.com/Insights/Market-Rankings/comScore-Reports-March-2015-US-Smartphone-Subscriber-Market-Share
- Is Xamarin Platform a Better Way for Creating Modern Mobile Apps? - https://tecordeon.wordpress.com/2015/03/19/is-xamarin-platform-a-better-way-for-creating-modern-mobile-apps-2/
- 5 Reasons to Use Xamarin - http://www.seamgen.com/blog/reasons-to-use-xamarin/
- Does Xamarin Really Decrease Time to Market of Your Mobile App? - https://blog.crystalnix.com/does-xamarin-really-decrease-time-to-market-of-your-mobile-app-b65323410006
- Native vs. Hybrid: Developing Cross-platform Mobile Apps - http://www.theappbusiness.com/native-vs-hybrid-developing-cross-platform-mobile-apps/
- Xamarin or Native Development Tools for iOS & Android Projects? - http://www.willowtreeapps.com/blog/xamarin-or-native-development-tools-for-ios-android-projects/

